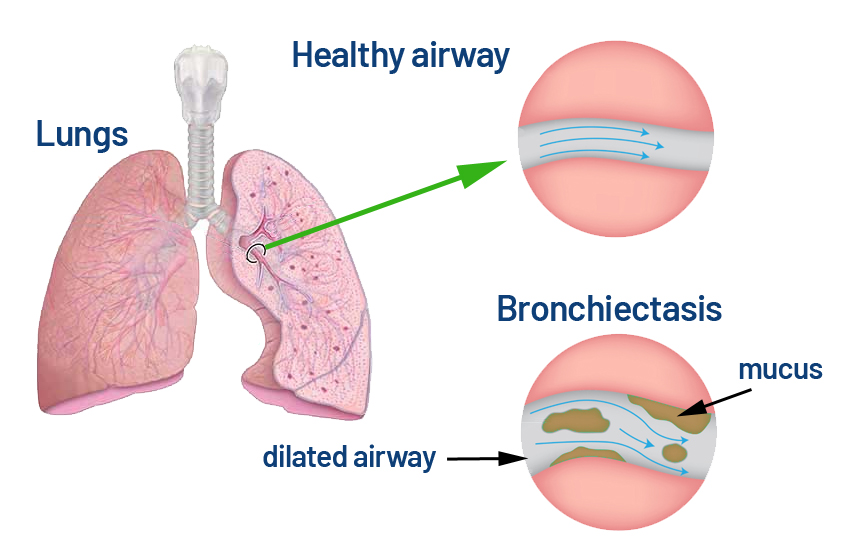
Bronchiectasis is a chronic lung condition where the airways become permanently widened and damaged, making it difficult to clear mucus. This can result from repeated lung infections, genetic conditions like cystic fibrosis, or immune system disorders. The build-up of mucus in the airways creates an environment for bacteria to thrive, leading to recurring infections and further airway damage.
The effects of bronchiectasis include chronic coughing with mucus, shortness of breath, fatigue, and recurrent chest infections. Over time, these symptoms can lead to lung function decline, reduced physical capacity, and complications like respiratory failure. Persistent infections may also strain the heart and reduce oxygen levels in the body.
COPD causes breathing difficulties, chronic coughing, and excessive mucus production. Emphysema damages the alveoli, reducing oxygen exchange, while chronic bronchiectasis leads to airway widening and frequent infections. These conditions worsen over time, making physical activity more difficult and increasing the risk of respiratory infections, heart disease, and lung failure. Symptoms like breathlessness and fatigue can significantly impact daily life.
Treatment focuses on managing symptoms, clearing mucus, and preventing infections. Chest physiotherapy, inhaled medications, and antibiotics are commonly used to improve lung function and control infections. In severe cases, surgery to remove damaged lung tissue or advanced therapies may be needed. With consistent care, many patients can manage the condition and maintain a good quality of life.